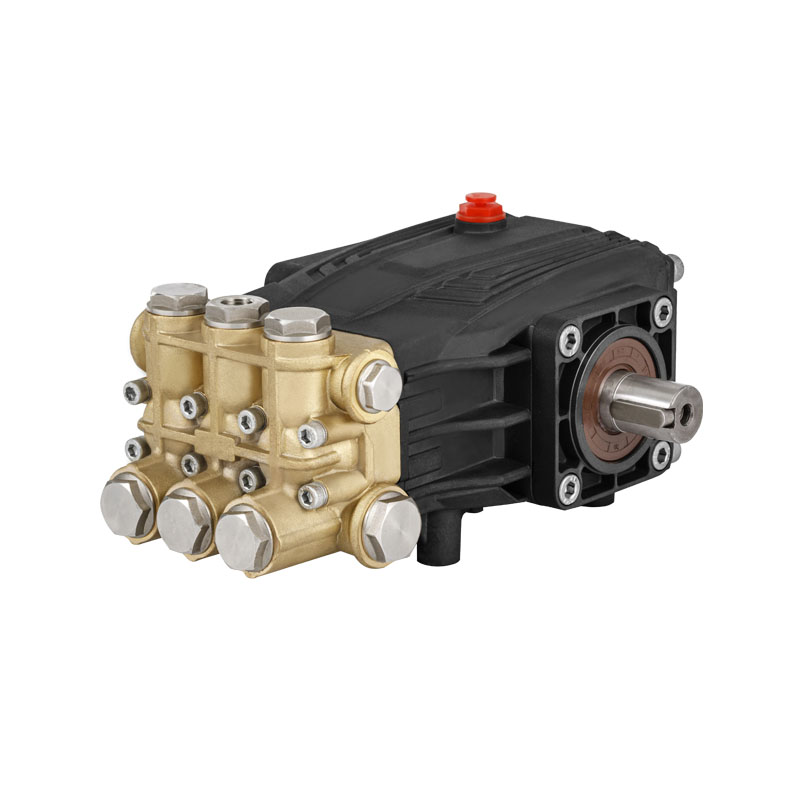
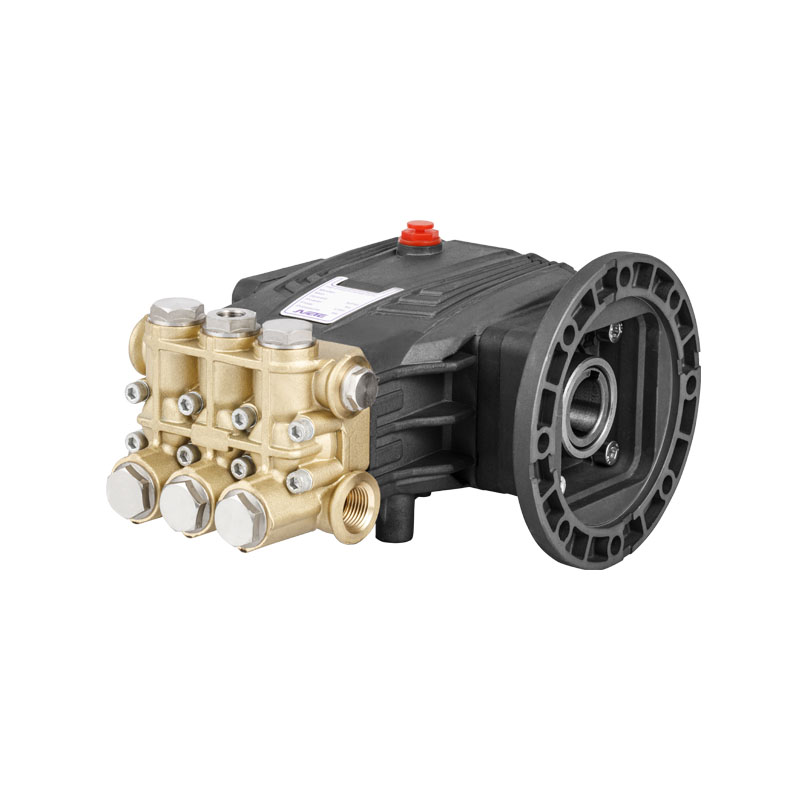
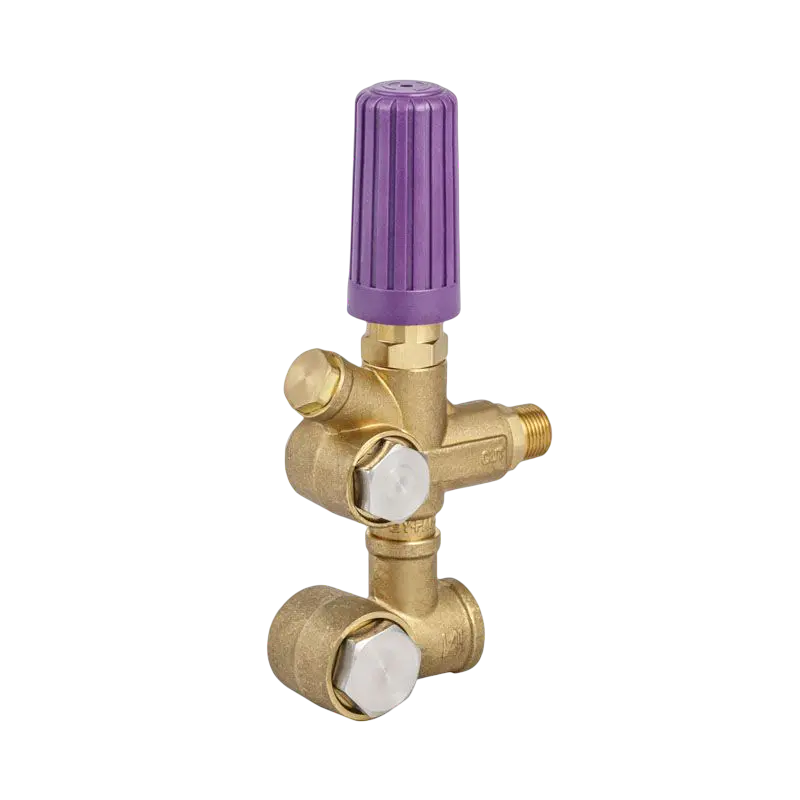
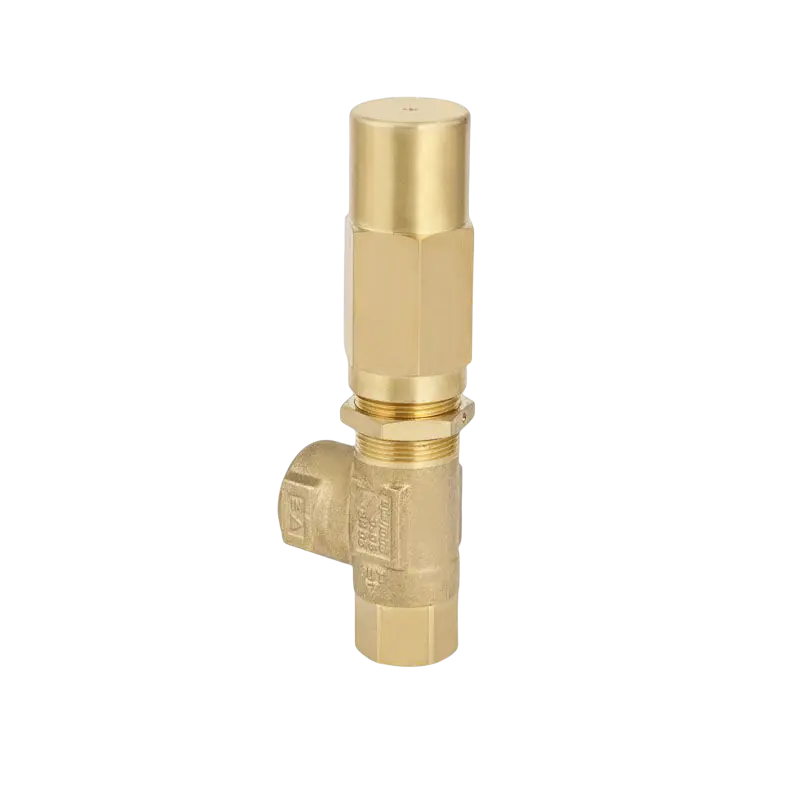
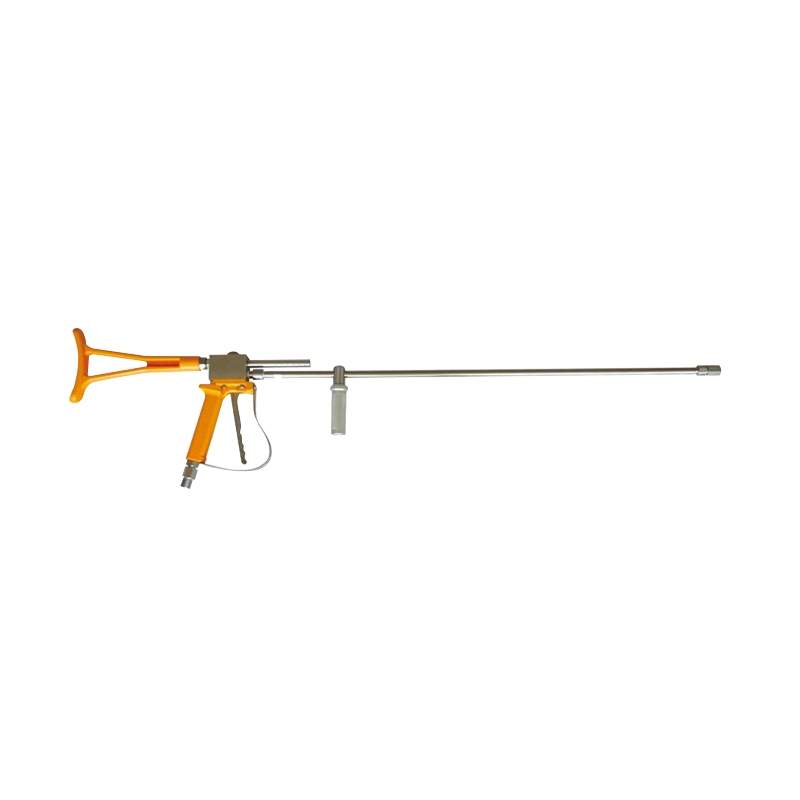
As industrial systems continue to rely on precise and powerful fluid control, the role of the High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve has become more critical than ever. Found at the core of numerous high-pressure pumping systems—from water jet cutting to oil and gas injection operations—this small but vital component ensures that pressurized fluid is properly regulated, directed, and contained. However, without routine maintenance, even the robust valve can become a point of failure.
The High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve endures repetitive high-stress cycles, rapid fluid movement, and in some cases, abrasive materials. These conditions make it susceptible to wear, erosion, and mechanical fatigue. As a result, industries are placing growing emphasis on proactive maintenance protocols to ensure the long-term performance and reliability of these valves.
Routine inspection is the line of defense in any maintenance strategy. Technicians are advised to regularly check each High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve for signs of leakage, vibration, and unusual noises during operation. These symptoms often indicate internal wear or improper seating, which can compromise the pump's efficiency and to pressure loss.
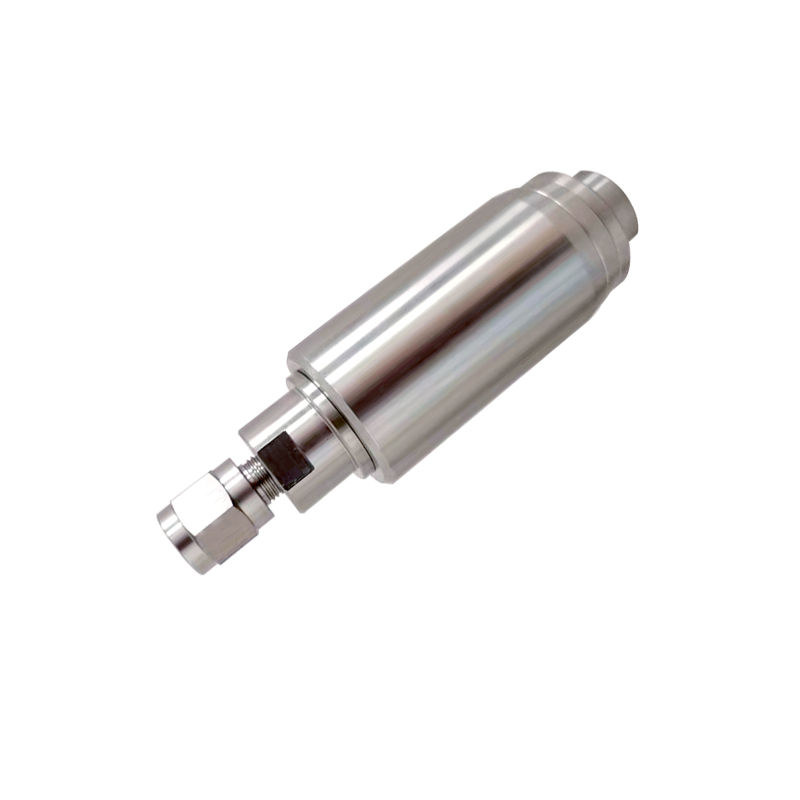
One of the common issues with a High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve is sediment buildup. Over time, mineral deposits or debris from the pumped media can accumulate around the valve seat and poppet, preventing proper closure. This leads to internal leakage and reduced system pressure. Cleaning and flushing the valve area as part of routine service helps prevent such buildup and maintains performance.
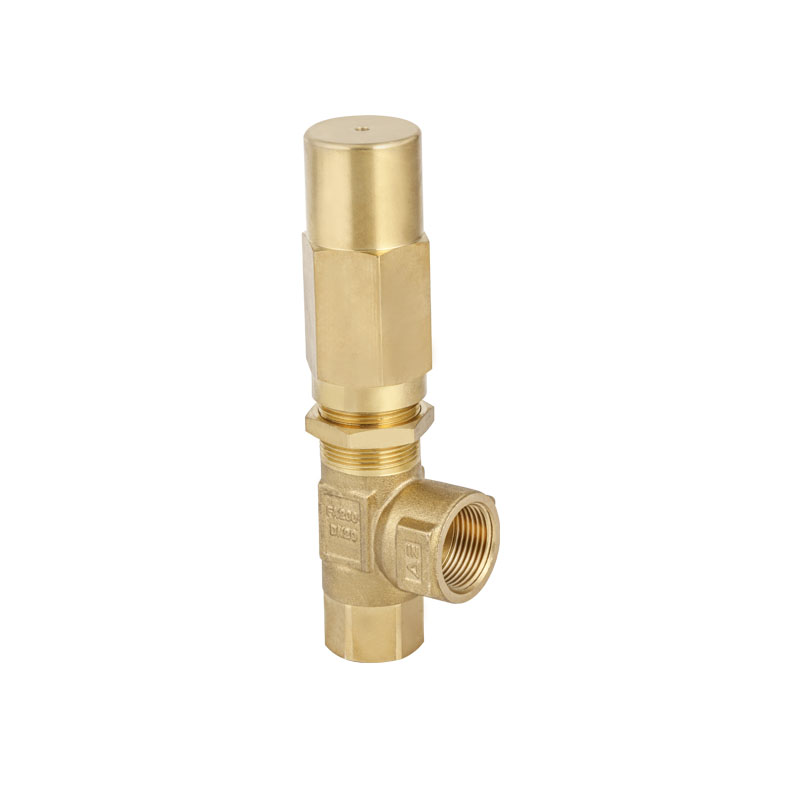

Valve spring integrity is another important factor. In every High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve, a tightly calibrated spring ensures the valve opens and closes at the correct timing and pressure. When this spring weakens or fails, the pump can experience backflow or pulsation issues. Maintenance teams must check spring tension periodically and replace any that show signs of deformation or corrosion.
A significant concern for operators is valve cracking or erosion, particularly in systems that handle corrosive or high-velocity fluids. To counteract this, many modern High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve designs incorporate hardened alloys or ceramic coatings. However, even advanced materials are not immune to long-term wear. Visual inspections using borescopes or disassembly can reveal early-stage pitting or cracking, allowing timely intervention before catastrophic failure.
Another essential aspect of valve maintenance is torque verification. Improperly tightened valve caps or seats can cause misalignment, leaks, or premature wear. Technicians servicing a High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve must follow manufacturer torque specifications precisely when reassembling the unit. Over-tightening can be just as damaging as under-tightening, to distorted components and performance issues.
With the rise of automation and IoT-enabled equipment, predictive maintenance is now being applied to valve systems as well. By integrating sensors into the High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve housing, operators can monitor flow rates, temperature fluctuations, and vibration patterns in real-time. This data helps predict wear trends and schedule maintenance before failure occurs, reducing downtime and improving system reliability.
Training and certification for technicians is becoming increasingly important in valve maintenance. A poorly serviced High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve not only shortens the lifespan of the pump but can also pose safety risks. Industry leaders now emphasize hands-on training and digital manuals that walk operators through proper disassembly, inspection, and reassembly procedures.
Furthermore, standardization in replacement parts has become a talking point in the industry. Using non-OEM components may reduce costs initially but can to misfitting or early degradation. Experts advise sourcing genuine parts when replacing elements of a High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve, particularly for high-pressure applications where precision is vital.
Environmental considerations are also influencing valve maintenance protocols. Leaking valves can to fluid wastage and environmental contamination, especially in chemical or oil-based operations. Regulatory bodies now mandate strict reporting and preventive maintenance schedules for any facility using a High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve in sensitive applications.
In summary, as the demand for high-pressure systems continues to grow across sectors, maintaining the integrity of every High Pressure Plunger Pump Valve has become essential. From routine inspection and cleaning to predictive analytics and specialized training, the industry is adapting rapidly to ensure these components perform flawlessly under pressure.












-2(1).png)




 English
English Español
Español